Understanding Thyroid Body Type Characteristics
- sherwood shea
- 6 days ago
- 4 min read
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, and overall health. For individuals affected by Graves' Disease, understanding the nuances of the thyroid body type can provide valuable insights into managing symptoms and improving quality of life. In this article, I will explore the concept of the thyroid body type, its characteristics, and practical ways to identify and support this unique physiological profile.
Thyroid Body Type Characteristics
The thyroid body type is often described as one of the three primary somatotypes, alongside the adrenal and pituitary types. It is characterised by a specific set of physical and metabolic traits influenced by the activity of the thyroid gland. People with this body type tend to have a faster metabolism, which can affect their weight, energy, and overall bodily functions.
Some common thyroid body type characteristics include:
Lean and slender physique: Individuals often have a naturally slim build with less body fat.
High energy levels: A faster metabolism usually results in increased energy and restlessness.
Warm body temperature: Due to increased metabolic rate, these individuals may feel warmer than others.
Rapid heartbeat: The thyroid influences heart rate, so a faster pulse is common.
Difficulty gaining weight: Despite a healthy appetite, weight gain can be challenging.
Fine, soft hair and skin: Hair may be thin and skin smooth but prone to dryness.
Nervousness or anxiety: The heightened metabolism can sometimes cause feelings of nervous tension.
Understanding these characteristics helps in recognising the thyroid body type and tailoring lifestyle choices accordingly. It is important to note that these traits can vary in intensity depending on thyroid function and overall health.

The Role of the Thyroid Gland in Body Type
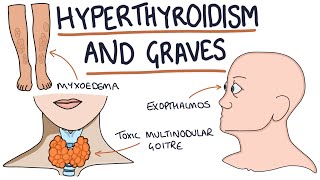
The thyroid gland, located in the neck, produces hormones that regulate metabolism. These hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), influence how the body uses energy. When the thyroid is overactive, as in Graves' Disease, the metabolic rate increases, leading to many of the thyroid body type characteristics.
The thyroid’s influence extends beyond metabolism. It affects:
Heart function: Increasing heart rate and cardiac output.
Digestive system: Speeding up digestion and bowel movements.
Muscle function: Affecting muscle tone and strength.
Mood and cognitive function: Impacting mental alertness and emotional state.
For those with Graves' Disease, the thyroid gland produces excessive hormones, which can exaggerate these effects. Recognising the signs of an overactive thyroid is essential for managing symptoms and maintaining health.
How do I know my thyroid type?
Identifying your thyroid body type involves observing physical traits and understanding your metabolic tendencies. Here are some practical steps to help determine if you fit the thyroid body type profile:
Assess your body shape and weight: Are you naturally slim with difficulty gaining weight despite a good appetite?
Monitor your energy levels: Do you experience bursts of energy or restlessness?
Check your body temperature: Do you often feel warmer than others around you?
Observe your heart rate: Is your pulse consistently faster than average?
Evaluate your skin and hair: Are your hair and skin fine, soft, or prone to dryness?
Note any nervousness or anxiety: Do you feel more anxious or tense without clear reasons?
Medical tests are crucial for confirmation. Blood tests measuring thyroid hormone levels (TSH, T3, T4) provide definitive information about thyroid function. Consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended for accurate diagnosis and personalised advice.

Managing the Thyroid Body Type with Graves' Disease
Living with Graves' Disease requires careful management of thyroid hormone levels and symptoms. Understanding your thyroid body type can guide lifestyle adjustments that support well-being. Here are some actionable recommendations:
Nutrition: Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole foods. Include adequate protein to support muscle mass and avoid excessive iodine intake, which can exacerbate thyroid activity.
Exercise: Engage in moderate physical activity that balances energy expenditure without causing excessive fatigue. Yoga and walking are excellent options.
Stress management: Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or mindfulness to reduce anxiety and nervousness.
Regular monitoring: Keep up with medical appointments and thyroid function tests to adjust treatment as needed.
Adequate rest: Prioritise sleep to help regulate metabolism and support recovery.
These strategies can help mitigate symptoms and improve quality of life for those with an overactive thyroid and the thyroid body type.
Supporting Research and Resources
The Robert James Graves Foundation is dedicated to improving the lives of individuals affected by Graves' Disease. Through funding vital research and providing crucial information, the foundation aims to enhance understanding and treatment options.
For those seeking more information on what is thyroid body type, the foundation offers comprehensive resources and support networks. Staying informed and connected with expert guidance is invaluable in managing this condition effectively.
By recognising the unique characteristics of the thyroid body type and applying practical management techniques, individuals can take proactive steps towards better health and well-being.
Understanding the thyroid body type is a key component in managing Graves' Disease. With the right knowledge and support, it is possible to navigate the challenges of this condition and maintain a balanced, healthy lifestyle.























Comments